Module Hardware
 Image credit: Unsplash: Umberto
Image credit: Unsplash: UmbertoTable of Contents
- In the following part i would like to present you the different components, which are inside of a PC, server or a notebook.
Computer case: Inside of the computer case you will find all following components of a Computer. The main idea is to protect the interior. It also contributes to a visual aspect of the computer.

CPU (central processing unit): The CPU is the brain of the computer. It does the logical calculations, processes data and passes informations to the other parts.
Motherboard: The motherboard or also known as mainboard connects all parts to each other and enables communication between each other components.

RAM (random access memory): It’s a temporary storage space to process data fast. The RAM is located nearby the CPU, to keep the latency as low as possible.

Storage device: A distinction is made between the HDD (hard disk drives) and the SSD (solid state drives). The HDD is working mechanical like a music turntable, while the SSD is a flash storage device. Both of them store data persistently.

PSU (power supply unit): The electricity from the power socket goes truth the PSU and is distributed to the various components.

GPU (graphics processing unit): It’s a specialized chip to calcultate all graphic outputs fast. A CPU can theoretically do the same, but it takes much longer than the GPU.

Cooling unit: All components that consume electricity, are generating heat. Because of this reason, you need a cooling unit to prevent damages on the different modules.

My Notebook
- Advanced questions about my notebook (ThinkPad X1):
How fast (in GHz) is the CPU you are using right now?
➡️Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10510U CPU @ 1.80GHz - 2.30 GHz
➡️On my motherboard is a SoC (System-on-a-Chip)
➡️ Southbridge / Northbridge / System-on-a-ChipHow many gigabytes of RAM are in the PC you’re using?
➡️16.0 GB (15.8 GB usable)What is/are the storage medium/media in your PC?
➡️500GB SSDWhere is the PSU in your PC? What about a laptop?
➡️Inside the PC
➡️External AdapterDo you have a GPU?
➡️iGPU in the CPU; Intel HD Graphics 620 (GT2)How does the cooling work in your device? What about a smartphone?
➡️My notebook is cooled from below by two fans
➡️Smartphones in general; Heatpipe, which transmits the heat to the outside
My future PC
- This are the parts that i would buy, if i would build my own PC. Link ➔ Digitec
Bits and Bytes
- Task – Bits and bytes
Say you have a gigabit internet connection (downstream). How many kilobytes can you download per second?
➡️1'000'000'000b / 800 = 125'000KB
➡️1'048'576B * 8 = 8’388’608bYou buy an HDD advertised with 1TB. How much usable space will the Windows operating system report you and why?
➡️If you have a 1TB HDD in your PC, then you have a real storage of 932GB. This is because the computer is working with binary numbers (1,024 bytes = 1kb).
Binary Digits
- Task – Decode the following binary sequences to text. Each character uses 8-bits.
01000001011011010110000101101110011011110111100000100000010101000110010101100001
➡️Amanox Tea
💡You have to read the binary code from the right to the left side. Then you encode the binary digits.
Example: 10101 ➔ (1 * 2^1) + (0 *2^2) + (1 *2^3) + (0 *2^4) + (1 _2^5) = 42
After this you can have a look to the ASCII-Table. 42 corresponds to _ .
➡️01011000 01100001 01110110 01101001 01100101 01110010
Johny Simulator
- Task – Multiplication with basic instructions
Create a sequence in the Johnny simulator that takes 2 numbers from any 2 registers, multiplies them and writes the result to another register.
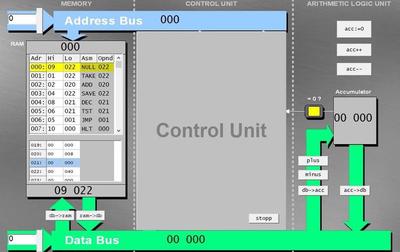
The Johny Simulator shows us, how a RAM calculation is working. Additions and subtractions can be performed directly, while multiplications have to be added up over several steps. In the simulator you have the opportunity to write and simulate programms.
Here is a list of the program commands:
●
TAKEThe value of the location (given by the absolute address) is transported to the accumulator.
●SAVEThe value of the accumulator is transported to the location given by the absolute address.
●ADDThe value of a location (given by the absolute address) is added to the value in the accumulator.
●SUBThe value of a location (given by the absolute address) is subtracted from the value in the accumulator.
●INCThe value of the location (given by the absolute address) is incremented.
●DECThe value of the location (given by the absolute address) is decremented.
●NULLThe value of the location (given by the absolute address) is set to zero.
●TSTIf and only if the location (given by the absolute address) has a zero value, the next macro instruction is skipped.
●JMPThe program is continued at the given location.
●HLTThe simulator shows a message that the program is finished.
Example programm for a multiplication 8 * 5 = 40
Inputs
Adress 020: 8 (Factor)
Adress 021: 5 (Factor)
Programm
1.
NULL 022; Set value of adress 022 to zero
2.TAKE 022; Transport value of adress 022 to the accumulator
3.ADD 020; Add the value of adress 020 to the value in the accumulator
4.SAVE 022; Transport value of the accumulator back to the address 022
5.DEC 021; Decrement value of the adress 021
6.TST 021; If the value 021 is equal 0, the next macro instruction is skipped
7.JMP 001; The programm continious at the location 001
8.HLT 000; End of program
Output
Adress 022: 40 (Product)
💡If everything has worked fine, then the adress line 022 should contain the value 40.
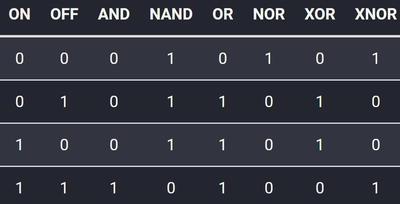
Transistors and Logic Gates
A transistor can be thought of as a gate that is either open or closed. When a transistor is on, then an electric current can flow through. And when it’s off, then no current flows. The first Transistor came up in 1947. This gates are very small but a lot faster than mechanical relay switches and vaacum tubes. A microprocessor contains more than five million transistors.
Logic gate function:
0 ➔ OFF ➔ no low voltage (0V)
1 ➔ ON ➔ low voltage (5V)

Cheat in CookieClicker
Score up faster with CheatEngine ➔ No more words needed

HDD & SSD in depth
If you ever shopped for HDDs, you probably stumbled across multiple flavors. For example, consumer-grade, NAS-grade and server-grade.
● What are the differences between those grades?
NAS-DISKS is a storage type, which is connected to a network that allows network users and clients to store and collect data from a central location. Normally a NAS-HDD is working permanent (24/7), but power-saving. NAS systems are flexible and scalable.
CONSUMER-DISKS storage grade devices are used for conventional use in a PC.
SERVER-DISKS have a lower probability of failure. They are designed for continuous operation.
● Are there grades/tiers for SSDs?
Consumer SSD➔ conventional ssd (low cost)Workstation SSD➔ 5-6 times faster than consumer-grade devicesEnterprise SSD➔ These SSDs are used for server applications in permanent operationCDN SSD➔ deliver the best balance of read performance, high reliability and low thermal load
● Search the web for 2 HDDs and SSDs that you would use in a consumer PC or server (1 for each use case).
Desired interfaces
● What are your desired interfaces in a consumer PC/laptop?
External
HDMIRJ45USB-AAUX In/OutThunderbolt 3
● What would you change for in a server?
In a server I would install 2x RJ45 for security reasons (redundancy).
| Name | Use case | Release | Bandwidth | Wires | Clock | Signaltype | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCA | Video, Audio | 1940 | 10 MHz | 1 | 768 kHz | Analog | 3m |
| VGA | Video Trans. | 1987 | 3 MBit/s | 14 | 60 MHz | Digital | 4m |
| DVI | Video Trans. | 1999 | 7.44 GBit/s | 29 | 165 MHz | Digital | 4.5m |
| PS/2 | Periphery | 1990 | 350 MHz | 4 | 16 kHz | Digital | 5m |
| RJ45 | Network | 1970 | 10 GBit/s | 8 | 160 MHz | Digital | 3m |
| USB-1.0 | Power, Data Trans. | 1996 | 1.5 MBit/s | 4 | 1 kHz | Digital | 5m |
| USB-2.0 | Power, Data Trans. | 2000 | 480 MBit/s | 4 | 24 kHz | Digital | 5m |
| USB-3.0 | Power, Data Trans. | 2008 | 5 GBit/s | 9 | 33 kHz | Digital | 5m |
| Thunderbold 3 | Power, Video, Audio, Network | 2015 | 40 GBit/s | 20 | 240 Hz | Digital | 2m |
| DP | Video Audio | 2006 | 77 GBit/s | 20 | 225 MHz | Digital | 1.8m |
| HDMI | Video and Audio | 2002 | 48 GBit/s | 19 | 150 MHz | Digital | 25m |
Internal
WIFIBluetooth
| Name | Use case | Release | Bandwidth | Contacts | Clock | Signaltype | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCI | Peripheral Component Interconnect | 1994 | 533 MBit/s | 16 | 66 MHz | Digital | |
| PCIe | Peripheral Component Interconnect Express | 2003 | 3940 MBit/s | 24 | 8.0 GHz | Digital | |
| SATA | Data exchange with hard disks | 2007 | 3 GBit/s | 7 | 6 GHz | Digital | |
| SAS | Mass storage interface | 2004 | 1200 MBit/s | - | 12 GHz | Digital | |
| WLAN | Network interface | 1980 | 300 MBit/s | - | 240 MHz | Digital | |
| Bluetooth | BT Device Connection | 1999 | 2 Mbit/s | - | 2 MHz | Digital |
Transferspeed and Bandwidth
● How much bandwidth is needed to stream a typical 2 hour Netflix 1080p movie (~6GB)?
● What bandwidth (upload/download) do you have at home and on your mobile phone?
Home WIFI:
Download: ~200MBit/s
Upload: ~350MBit/s
Mobile phone (4G):
Download: ~21MBit/s
Upload: ~1.5MBit/s
VR Headsets
● What do you think are problems when placing screens this close to our eyes?
VR glasses trick the brain as well as the eyes. The main problem is, that a VR headset is very close to the eyes. If you are using this devices for too long, it can lead to myopia or to sleep rhythm disorders. Especially the blue light is said to be harmful for our eyes.
● What specifications should the display fullfill to enable a good experience?
For a good virtual experience you should have a 4K-Display with 3840 x 2160 pixels.
Audio Interfaces
● What interfaces are used to play surround sound?
- S/PDIF
- HDMI
other Audio Interfaces
- AES/EBU
- MADI
- ADAT
- TDIF
- Wordclock
● What are common codecs?
- PCM (Puls-Code-Modulation
- MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3)
- AAC (Advanced Audio Coding)
- Vorbis
- WMA (Windows Media Audio)
Display
● Why did manufacturers ditch the CRT and plasma technologies?
The former advantages of plasma technology, namely fast image changes, better colors and strong contrasts, are now all surpassed by OLED. CRT screens are very old and require an enormous amount of space, which is no longer time compliant. The vaakum tube in a crt display is under a large negative pressure. Because of this reason, crt screens must be made of glass, which can withstand this pressure. Due to the glass housing, crt screens weigh a lot.
● What are the pros and cons of LCD and OLED compared to eachother?
A LCD display is brighter than an OLED Display. For example, this can be crucial for a mobile phone, if you are using your smartphone outside a lot.
OLED displays promise higher contrast images than LCD displays. This is because each individual pixel can be adjusted in brightness, whereas LCD screens can only be darkened in areas.
Office Workplace
● How should the PC perform? Did you choose a laptop or a workstation?
I plan to move to Bern in the next time. For this i will need an office workplace. The idea is to buy a notebook. Maybe i create my own notebook with the knowledge i got in the last few days.
Here is alist of the required hardware:
Hardware
NotebookMouseKeyboardDocking Stationcurved display (OLED)Headsetconfortable chair & adjustable tableeGPU
● What interfaces do you need?
Interfaces
HDMIUSB-3.1AUX In/OutThunderbolt 3 or 4BluetoothWIFICellular interface
● Is an upgrade possible down the road?
Upgrades
Depending on the notebook I buy, maybe yes.
eGPURAM (if not soldered)CPU
Cooling Systems
● What metric should be high for a fan on a heatsink?
➔ RPM
● What metric should be high for a case fan?
➔ performance
● Why do servers often use small fans instead of bigger ones?
On the one hand, it is important to save as much space as possible when building a server, and on the other hand, fewer programs and calculations are carried out on a server than on a desktop PC, which means that the processor also has to be cooled less.