Cloud Security in AWS
 Image credit: Unsplash: Nathy dog
Image credit: Unsplash: Nathy dogIn this module I will learn about Cloud Security in AWS. Here you will find several tasks or summarizations about the topic.
Table of Contents
Section 1: Course Introduction
Security is the practice of safeguarding intellectual property from unauthorized access, use, or modification.
The CIA triad is a fundamental concept in information security, comprising three core principles:
- Confidentiality: Limiting access to information to authorized users and preventing access by unauthorized persons.
- Integrity: Ensuring the consistency, accuracy, and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle, including the origin or source of the data.
- Availability: Ensuring that information resources are readily accessible when needed.
The CIA triad faces challenges in modern IT environments due to the large volume of information to be protected, the diverse sources of data, and the variety of formats used.
Security in the AWS cloud
AWS tries to make security as familiar as what we are doing day by day. Security is of utmost importance, especially in a cloud environment. Existing security models used in on-premises environments can be applied to the cloud. AWS offers various services and tools to enhance security, providing controllability, auditability, and visibility into cloud resources and workloads. The ability to work in an agile way and automate processes is especially important for incident response.
Security design principles
- least privilege
- enable traceability
- secure all layers
- automate security
- protect data in transit and at rest
- prepare for security events
- minimize attack surface
AWS Well-Architected Framework
AWS follows the Shared Responsibility model (SRM), where responsibilities are divided between AWS and its customers.
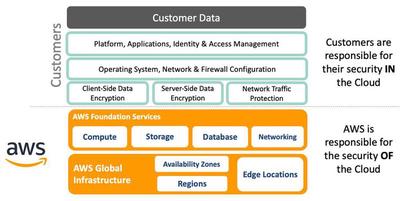
AWS is responsible for safeguarding the global infrastructure that hosts all AWS Cloud services, including hardware, software, networking, and facilities. As an AWS customer, you can securely provision various resources in the AWS Cloud, such as virtual machines, storage, databases, and desktops. Customers are responsible for securing their data, operating systems, networks, platforms, and other resources created in the AWS Cloud. Customers are accountable for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data in the cloud, and for meeting specific business and compliance requirements for their workloads.
The division of responsibilities varies depending on the type of AWS services used, implying different levels of responsibility for AWS and the customers.
Section 2: IaM
Authentication vs. Authorization
- Authentication is the process of identifying the users and validating who they claim to be.
- Authorization is the process (after authentication) to give the user access to specific resources (mostly role-based)
AWS Identity and Access Management (IaM) Recap
AWS uses IaM for authentication and authorization in the cloud. The following entities are relevant:
- Users: Indentity with long term credentials (pw/access key)
- Groups: A collection of users, apply permissions to a collection of users
- Roles: Identity with short term credentials, can be assumed by entities like users, services, accounts etc.
- Policies: An object in AWS that defines permissions (on AWS resources), can be attached to users, groups and roles
Amazon Cognito for Authentication
Amazon Cognito is a service from AWS that provides authentication, authorization, and user management for web and mobile applications. It consists of two main components: User Pools and Identity Pools.
A user pool serves as a user directory that manages the login and registration process for an application. Users can sign in either directly through a user pool, or federate through a third-party identity provider (IdP). The main purpose of a user pool is the authentication of users by storing user data and providing users with access tokens. User Pools are not directly associated with AWS resources and do not handle the authorization of AWS services (directly).
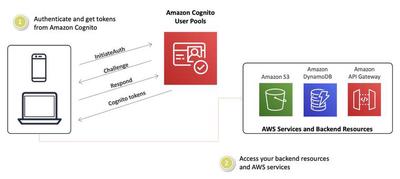
An Identity Pool allows temporary AWS credentials to be assigned to users (authenticated or unauthenticated) for example from a user pool, or other IdPs to grant access to AWS resources. An Identity Pool is focused on authorizing and managing AWS credentials.
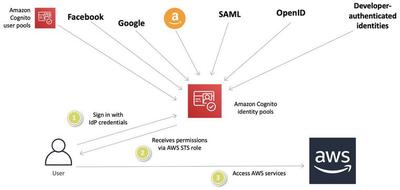
Different example use cases:
| example App | pool? | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blogging platform | User pool | A blogging platform where users can write articles, comment and manage their profiles. | A user pool is ideal for handling user registration and authentication. Users can log in, reset their password, and update their profiles. Since the interactions are mainly at the application level and do not require direct AWS permissions, an Identity Pool is not necessary. |
| Guest access to news app | Identity pool | A news app where unauthenticated users (guests) can read articles and watch videos from a media archive. | An Identity Pool can be used to grant temporary AWS permissions to guests to access media content in AWS services. Since there is no authentication requirement for access, no user pool is needed. |
| Photo sharing app | both | A mobile photo sharing app where users can upload their photos, which are stored in an S3 bucket, and share them with others. | A User Pool authenticates users and manages their credentials. After successful authentication, the Identity Pool provides temporary AWS permissions that allow the authenticated user to upload or download photos in an S3 bucket. |
Section 3: Detective Controls
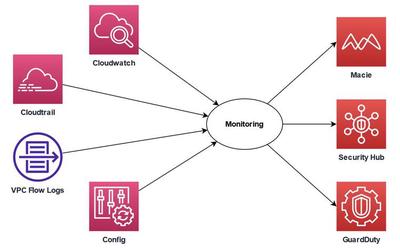
Amazon GuardDuty for Threat Detection
Amazon GuardDuty is an intelligent threat detection service for AWS accounts and workloads. It uses threat intelligence and machine learning to detect anomalies and suspicious activities, such as unauthorized deployments. When a threat is found, alerts are sent to the GuardDuty console and AWS CloudWatch Events for integration with existing services or systems.
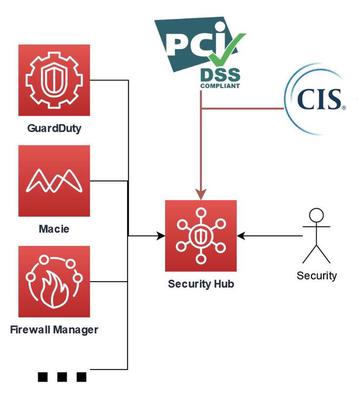
AWS Security Hub for Prioritizing Findings
AWS Security Hub is a consolidated view of security. It uses different AWS services as inputs (e.g. GuardDuty, Macie, Firewall Manager, etc.). It also support third party insights. In security hub you have the possibility to evaluate the security in the cloud with different securiry standards. The insights and findings can be forwarded to EventBridge for incident responses.
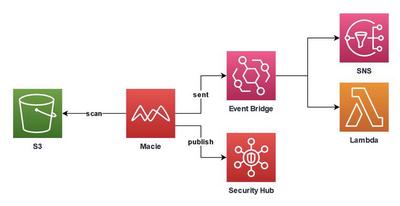
Amazon Macie for Data Monitoring
Amazon Macie can be used to analyze S3 buckets for sensitive data such as names, addresses, and credit card numbers. It also evaluates whether an S3 bucket is publicly accessible and whether it is encrypted or not. The analyses are be performed as jobs. They can be shedulded on personal preferences. The results can be published to security hub or even to event bridge to take action in an automated way.
Section 4: Infrastructure Protection
Securing Your Compute Resources
In AWS you have different opportunities to limit access to resources on the network level. The most common ways are:
- Firewall on the host (e.g. netfilter on linux)
- Security Groups
- Subnet access control lists
- Web application firewall (WAF)
- Network firewall
- …
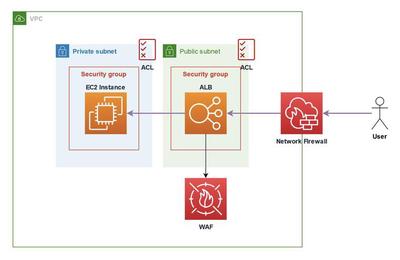
Securing compute resources on AWS | Screenshot
WAF for Traffic Filtering
A web application firewall operates at layer 7 and is capable of filtering the http protocol. The most common method of catching violations is to block requests or block them above a certain threshold. Possible filter rules are:
- filtering based on headers
- Query parameters
- HTTP-Methods
- URI path
- IPs
- http body (e.g. strings, size or SQL injection)
AWS WAF
AWS WAF is a Web Application Firewall managed by AWS and is organized in Web Access Control Lists (Web ACLs). Web ACLs can be associated with different AWS services like:
- ALBs
- API Gateways
- AppSync
- CloudFront
After a WAF is associated, every request gets checked based on the configured rules.
AWS Shield for DDoS Protection
AWS Shield is a managed DDoS protection service that safeguards web applications that run on AWS. AWS Shield provides always-on detection and automatic inline mitigations that minimize application downtime and latency.
Section 5: Data Protection
Amazon S3 spotlight
Amazon S3 is an object storage service in AWS that enables storage, retrieval, and management of data in the cloud. It uses a flat namespace schema with buckets and keys and provides API access for CRUD operations. It is used for static websites, backups, archiving, and data analytics etc. -S3 data is fully private to an account, and public access is blocked by default
- Ability to encrypt your data and have AWS manage the keys
S3 Protection via resource-based policies
Default Privacy and Access Control: Amazon S3 resources are private by default, only accessible by the owner. Access can be controlled through policies and Access Control Lists (ACLs).
Types of Access Control Mechanisms: Amazon S3 supports two groups of access control: resource-based (bucket policies, bucket ACLs, object ACLs) and user-based (IAM user policies). ACLs grant read or write access to groups of users. Policies enable centralized management.
Bucket Policies: Bucket policies in Amazon S3 can add or deny permissions within a single bucket. They allow for flexibility in granting access to users within your AWS Account or other AWS accounts, centralizing the control of permissions.
Use cases
Object ACLs:
- Grant access to individual objects
- Access objects owned by another account
Bucket ACLs:
- Grant log delivery group write permissions to bucket
Bucket policies:
- Offer a larger range of permissions than bucket ACLs
- Provide cross-account access to bucket
IAM identity-based policies:
- Manage permissions by creating users and groups and attaching policies
Protection via encryption
Encryption primer
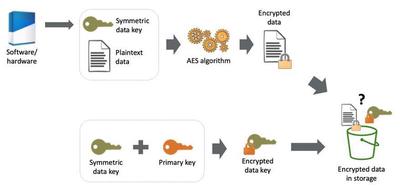
Data encryption is typically done using a symmetric data key generated by software or hardware, preferable for encrypting large amounts of data. This key is applied to the data using an algorithm like AES, resulting in indistinguishable ciphertext. The encrypted data can be stored on platforms like AWS or on-premises.
To decrypt the data, the symmetric data key must be available to authorized users. It can’t be stored with the encrypted data as it would compromise security. The best practice is to encrypt the symmetric data key with a KMS key, allowing it to be stored with the encrypted data in the same location, maintaining similar durability characteristics.
Supported Encryption by Amazon S3
Amazon S3 supports Client-side encryption (CSE) and Server-side encryption (SSE). CSE means that the customer encrypts his data by self with an Encryption Software and then publish it to AWS. If you use Server-side encryption then AWS manages the encryption and decryption proccess. Each approach has its own advantages.
When selecting the right enryption solution for data in AWS then three question should be come up:
- Where will the keys be stored? Will they be stored by your own hardware or using hardware provided by AWS?
- Where will the keys be used? Will they be used by the client software or on AWS?
- Who will manage the keys? Do you want to assign user- or application-level permissions or have AWS manage permissions?

S3 Client-side encryption
Only the encrypted version of the data is stored in S3, ensuring that AWS never sees the unencrypted content. The client maintains the keys and ecrypts and decrypts the data with
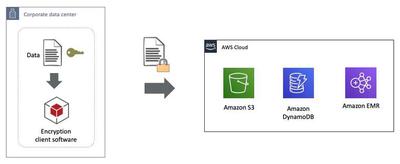
S3 Server-side encryption: Three different approaches
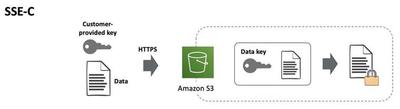
With SSE-C in Amazon S3, you provide an encryption key for S3 to handle encryption and decryption. You manage only this key, not the encryption process. S3 doesn’t store your key but keeps a salted HMAC value to validate requests. This HMAC can’t decrypt data. If you lose the key, you lose access to the object.
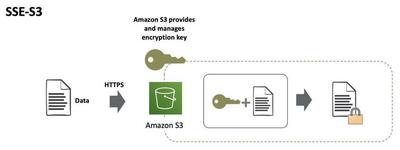
SSE-S3 is an AWS managed approach. Amazon S3 encrypts each object with a unique key. As an additional safeguard, it encrypts the key itself with a Primary key that it rotates regularly. Amazon S3 server-side encryption uses one of the strongest block ciphers available to encrypt your data, 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256).
SSE-KMS encrypts Amazon S3 objects using AWS KMS keys, offering greater benefits than SSE-S. AWS KMS employs envelope encryption with two keys:
- a data key for object encryption
- a master AWS KMS key for the data key’s encryption.
This process enhances security against unauthorized access. With SSE-KMS, users get an audit trail of key usage in CloudTrail, the choice to create or use a default encryption key, and the ability to enforce key policies and import personal key material, granting more control than SSE-S3.
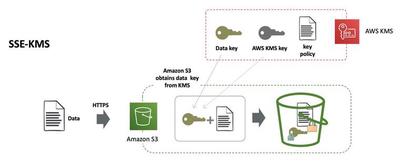
SSE-KMS | Screenshot
Best practices for protecting data in Amazon S3
- Enforce encryption at rest.
- Separate data based on different classification levels.
- Review S3 bucket and object permissions regularly.
- Define your data retention requirements.
- Implement secure key management.
AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
AWS KMS is a managed service that lets you create, control, and securely store encryption keys using FIPS 140-2 validated hardware. Integrated with most AWS services, it employs envelope encryption and a two-tiered key hierarchy. You can encrypt/decrypt data under keys you control, set key usage policies, and monitor usage through AWS CloudTrail. The key never leaves AWS KMS, minimizing data key compromise risks.
When hardware is FIPS 140-2 (Federal Information Processing Standard Publication 140-2) validated, it means the hardware has undergone a rigorous testing process and is approved to be used in government and regulated industries for securing sensitive or classified information.
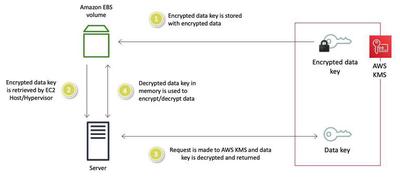
- Amazon EBS obtains an encrypted data key under a CMK through AWS KMS and stores the encrypted key with the volume metadata.
- Encrypted data key is retrieved from storage by the servers that host EC2 instances.
- A call is made to AWS KMS over SSL to decrypt the encrypted data key. AWS KMS identifies the CMK, makes an internal request to an HSA in the fleet to decrypt the data key, and returns the key back to the customer over the SSL session.
- The decrypted data key is stored in memory and used to encrypt and decrypt all data going to and from the attached EBS volume. Amazon EBS retains the encrypted data key for later use in case the data key in memory is no longer available.
HTTPS - CA - SSL Certificate
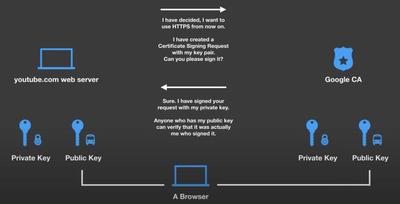
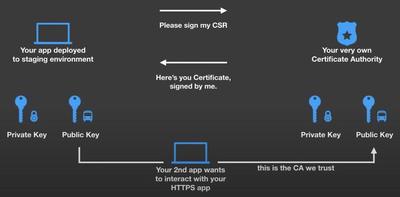
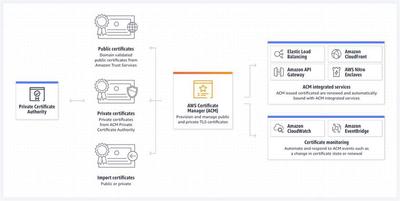
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) lets you easily provision, manage, and deploy public and private Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) certificates for use with AWS services and your internal connected resources. With ACM, you no longer need to spend time purchasing, uploading, and renewing SSL/TLS certificates manually. This makes it simpler to secure your applications and services with SSL/TLS encryption and ensures that your certificates are always up-to-date.
AWS Secrets Manager for Credentials Management
Secret management best practices
- Safely and securely store secrets in a central repository
- Audit log for the use and misuse of secrets
- Secrets rotation on a regular schedule
- Access control of secrets
AWS Secrets Manager for Credentials Management
AWS Secrets Manager is an AWS tool designed for secure management of sensitive data like passwords and API keys. Users can centrally store, control access, and fetch these secrets, eliminating the need for hardcoded credentials in code. The service offers automatic secret rotation, enhancing security.
Choose AWS Secrets Manager for:
- Centralized and secure management of secrets.
- Compliance with regulatory standards.
- Automatic and safe secret rotation.
- Monitoring secret usage without disrupting applications.
- Avoiding embedded secrets in code or configs.
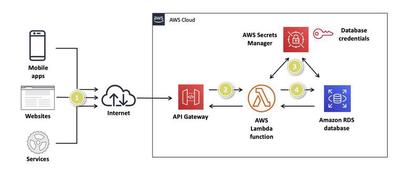
AWS Secret Manager in Action | Screenshot
Section 6: Application Security
Amazon Inspector
Amazon Inspector is an automated security assessment service that helps improve the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS. Amazon Inspector automatically assesses applications for vulnerabilities or deviations from best practices. After performing an assessment, Amazon Inspector produces a detailed list of security findings prioritized by level of severity. These findings can be reviewed directly or as part of detailed assessment reports which are available via the Amazon Inspector console or API. Amazon Inspector is an agent-based service where you deploy the Amazon Inspector agent on the Amazon EC2 Instances running the applications you want to assess.
The service provides the following benefits to AWS Customers:
- It automates security assesments
- It provides the knowledge and best practices in security from AWS itself
- It also provides guidance on resolving security findings

Getting started with the AWS Inspector | Screenshot
An assessment template is a configuration that you create in Amazon Inspector to define your assessment run. It includes a rules package that is used to evaluate instances, the duration of the assessment run, and Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topics to which you want Amazon Inspector to send notifications about assessment run states and findings. A rules package is a collection of security tests. Amazon Inspector has many rules packages, including common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE), Center for Internet Security (CIS) Operating System configuration benchmarks, and security best practices.
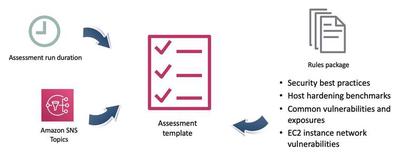
Section 7: Incident Response
What is an incident?
- An unplanned interruption or reduction in the quality of a service
- Failure of a configuration item that has not yet affected a service
- All incidents are events, but NOT all events are incidents
Incident Response
Incident response is the methodology an organization uses to respond to and manage a security breach or cyberattack. It is an organized approach to addressing and managing the aftermath of an attack. Even with extremely mature preventive and detective controls, your organization should still put processes in place to respond to and mitigate the potential impact of security incidents.
- Detect potential impacts
- React and recover from security incidents
- Automate Security
- Etablish control
IR on AWS
Incident response in the AWS Cloud is more efficient in terms of cost, speed, effectiveness, and management. AWS enhances your capacity to detect, react, and recover. AWS offers unique capabilities for investigations:
Automation with APIs: Routine tasks during incident response can be automated. For instance, a single command can alter security groups to isolate an instance.
Forensics and Data Capture: Amazon EBS snapshots and Amazon EC2 APIs allow you to capture disk images and system states for investigation purposes.
Environment Creation:AWS CloudFormation lets you swiftly set up a secure and isolated environment with the essential tools for in-depth forensic analysis.
Detailed Logging: AWS offers detailed logs for specific services, highlighting actions like file access and changes, aiding in understanding incidents and informing remediation steps.
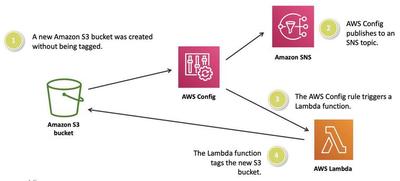
AWS Config for Responding to Incidents
AWS Config continuously monitors and logs configuration changes of your resources. Upon detecting changes, it sends notifications and can even trigger an AWS Lambda function for automated responses. Furthermore, it integrates with other AWS services, ensuring streamlined remediation of issues.
With AWS Config rules, you can continuously monitor and assess your resources to ensure they align with your security guidelines, best practices, and compliance standards. AWS offers many ready-to-use managed rules that need little or no setup. For instance, there’s a rule in AWS Config to confirm that all Amazon EBS volumes in your account are encrypted.
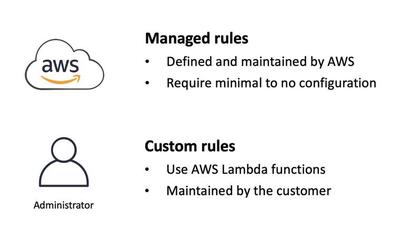
Some managed rule examples include:
- Checking if all attached Amazon EBS volumes are encrypted.
- Verifying that all Amazon EC2 instances are part of a VPC.
- Ensuring resources have the expected tags.
- Confirming security groups deny unsolicited incoming SSH traffic.
- Validating that AWS CloudTrail is active in your AWS account.
- Checking if the IAM users' password policy meets certain criteria.
For more tailored needs, you can craft custom AWS Config rules for example by using AWS Lambda Functions which can take actions when a specific incident appears.
Section 8: What’s Next
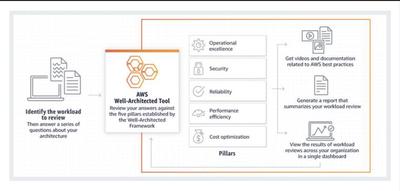
AWS Well-Architected Tool
The AWS Well-Architected Tool is a self-service tool that is designed to help customers review AWS workloads at any time, without the need for an AWS Solutions Architect. The Tool provides clear guidance to make architectural, design, and implementation decisions, increasing the security, efficiency and reliability of cloud implementations.
The AWS Well-Architected Framework includes five pillars, each with design principles and best practices. The five pillars represent:
- Operational Excellence.
- Safety and Security
- Reliability
- Performance Efficiency
- Cost Optimization
AWS recommends regular reviews of its own architectures against the five pillars above.